You’ve seen it on your morning walk. Maybe even ordered one before your first call.
That bright green matcha latte at Starbucks or your local café? It’s more than a caffeine fix; it’s a signal of what people want: energy from plants, cleaner labels, and ingredients they can pronounce.
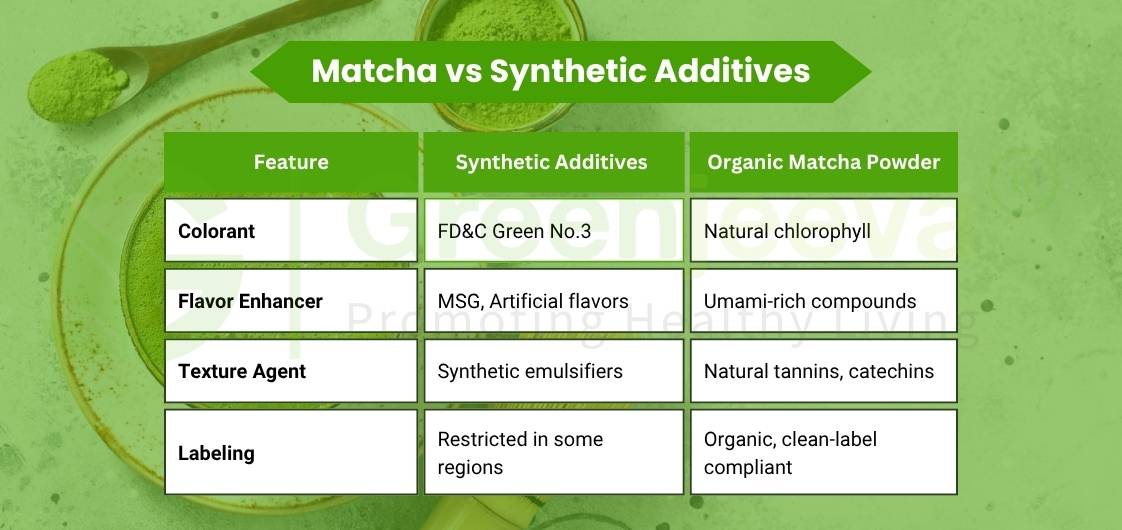
If you work in formulation, sourcing, or product development, you’re likely feeling that shift firsthand. The same organic matcha powder showing up in café menus is now being evaluated in labs, for its natural color, sensory profile, and ability to replace synthetic additives in everything from beverages to beauty powders.
This blog breaks down how organic matcha powder is replacing synthetic additives across food, beverage, and cosmetic formulations. We also cover what it contains, how it performs functionally, and what sourcing teams should know when procuring it in bulk.
What Is Organic Matcha Powder Made Of?
Matcha is a powdered form of specially grown and processed green tea leaves. Unlike regular green tea, matcha involves shade-grown leaves that are stone-ground into a fine powder. The organic variant is cultivated without synthetic inputs, aligning with clean-label standards.
From a formulation perspective, organic matcha powder contains:
Natural Caffeine – Acts as a plant-based stimulant in energy blends
Chlorophyll – Offers natural green coloring, a potential alternative to synthetic dyes
Catechins (EGCG) – Contribute to natural preservation and stability in certain blends
L-theanine – Known for balancing sensory impact
Tannins – Useful in cosmetic applications for texture and natural astringency
These components make organic matcha a versatile, multi-role ingredient in modern formulation strategies.

How Does Organic Matcha Perform in Product Formulations?
1. As a Natural Colorant
Matcha’s rich green hue is widely used in replacing synthetic green dyes in products like:
– Ready-to-drink beverages
– Ice creams and frozen desserts
– Plant-based snacks
– Soap and cosmetic bars
Its chlorophyll content delivers both visual appeal and label-friendly positioning.
2. As a Flavoring Agent
The umami-rich, slightly bitter taste of matcha allows it to serve as a natural flavor enhancer—especially in:
– Nutritional bars
– Functional beverages
– Herbal supplements
– Toothpastes and face masks (for sensory texture)
3. As a Functional Ingredient for Sensory Balance
The natural caffeine and L-theanine present in matcha contribute to the development of product experiences tied to energy and focus. This is especially relevant in:
– Pre-workout blends
– Adaptogenic formulas
– Functional beverage bases
Matcha is often used in place of synthetic stimulants or artificial sweeteners in these categories.
4. As a Natural Stabilizer or Shelf-Life Enhancer
While not a preservative, matcha’s catechins can support blend stability, particularly in:
– Powdered blends
– Capsules and sachets
– Emulsions and creams
It helps maintain color and sensory consistency during shelf life, reducing reliance on artificial stabilizers.
What Types of Industries Are Using Organic Matcha Powder?
Organic matcha powder is in demand across several industries, including:
Functional food and beverages – For natural energy, flavor, and color applications
Nutraceuticals – Used in capsule blends, tablets, and herbal powder mixes
Clean beauty and personal care – For creams, scrubs, and natural color-based cosmetics
Specialty bakery – For unique flavor, color, and label appeal
Pet nutrition (plant-based) – In premium, clean-label formulations
Bulk Sourcing and Industrial Considerations
If you’re sourcing for industrial-scale production, here are key aspects to consider:
1. Grade and Mesh Size
Culinary, ceremonial, and industrial grades differ in texture, flavor, and color. Industrial use usually prefers a finer mesh size for better solubility and blending.
2. Moisture and Microbial Limits
Ensure the powder has moisture content under 10% and meets microbial load limits relevant to your application—particularly for food and personal care use.
3. Compliance Documentation
Buyers in the U.S. and Canada typically require:
– Organic certifications (e.g., USDA Organic, COR Certificates)
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
– Pesticide residue test reports
– Allergen statements etc.
4. Shelf Life and Packaging
Standard shelf life is 18–24 months in airtight, light-resistant packaging. Bulk suppliers should offer heat-sealed, food-grade packaging options.
 Matcha Market Trends and Opportunities
Matcha Market Trends and Opportunities
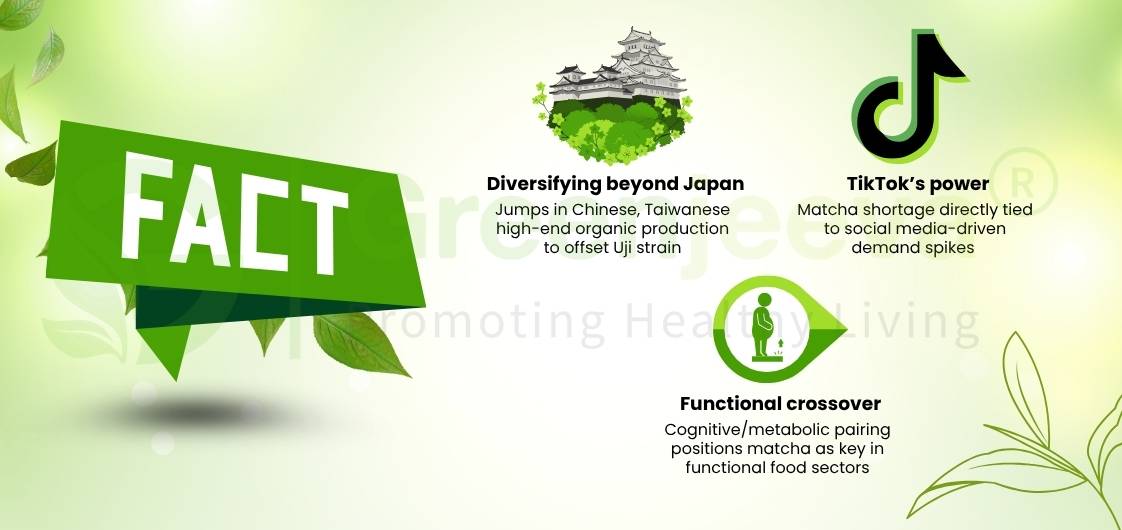
Data from October 2023 through early 2025 shows that the North American market has experienced:
– Steady growth in matcha applications across RTD drinks, clean-label snacks, and beauty powders
– Rise of private-label wellness brands requesting organic, multi-functional ingredients
– Increased demand for natural colorants and stimulant alternatives
– Notable product launches in functional beverages and beauty segments with matcha as a featured ingredient
The demand is driven by both consumer behavior and institutional buyers pushing for clean-label compliance and natural ingredient decks.
FAQs for Industrial Buyers
Q1. Can organic matcha powder be used in both food and cosmetic formulations?
Yes. Its natural color, fine texture, and plant-derived profile make it suitable across a range of applications.
Q2. What should procurement teams ask when sourcing bulk matcha powder?
Key questions include: origin, mesh size, compliance certifications, lab testing, moisture content, and packaging specs.
Q3. Is there a standard dose for product applications?
The inclusion rate depends on the format—beverages may use 1–2 g per serving, while cosmetics may use 0.5–1% concentration.
Q4. What makes organic matcha different from conventional matcha?
Organic matcha is grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers and comes with third-party certification, important for clean-label positioning.
Q5. How stable is matcha in blended formulations?
When stored and processed correctly, it offers good color and flavor retention over typical shelf-life durations.
Final Thoughts
Organic matcha powder is emerging as a reliable clean-label alternative to synthetic additives across product categories. Its natural color, sensory properties, and formulation stability give it a multifunctional role in today’s industrial ingredient systems. Whether you’re designing functional foods, beverages, or cosmetic formulations, matcha offers a plant-based solution aligned with evolving product standards and consumer expectations.
Source Organic Matcha Powder from a Supplier You Can Trust
At Green Jeeva, we offer bulk organic matcha powder that meets industrial-grade standards with complete documentation, price, and inventory transparency. Whether you’re developing functional beverages, clean-label foods, or botanical cosmetic lines, we support your sourcing goals with reliable supply and end-to-end service.
Request a quote or register in our B2B ecommerce platform to check real-time availability.