Description
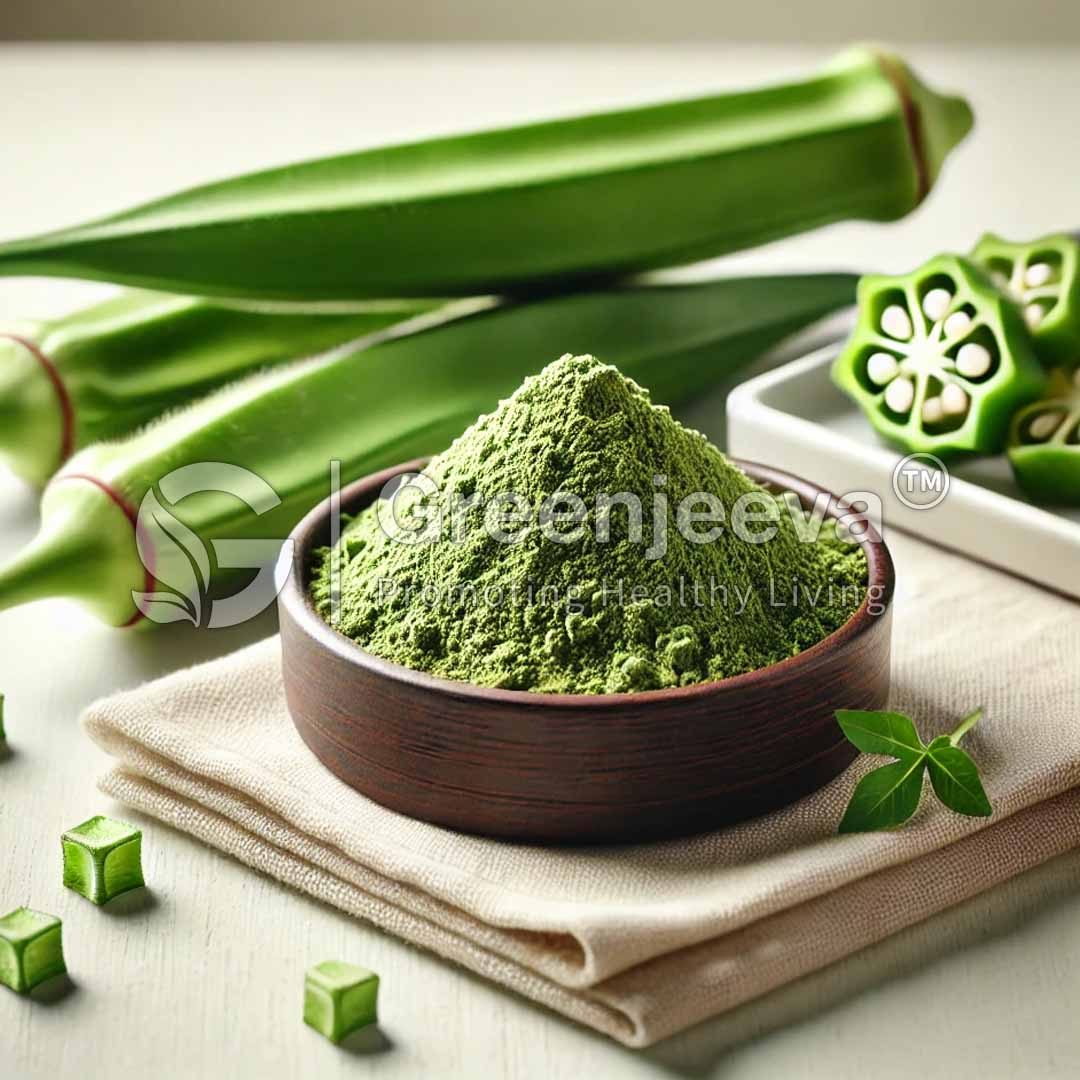
Botanical Name: Abelmoschus esculentus
Plant Part Used: Fruit
Processing Method: Extraction
Okra Extract Powder 10:1 is a concentrated extract derived from the fruit of Abelmoschus esculentus, commonly known as okra. The 10:1 extraction ratio means that 10 parts of raw okra fruit are used to produce one part of extract, ensuring a potent and high-quality powder. This extract is valued for its potential benefits in supporting digestive health, lowering blood sugar levels, and promoting overall wellness.