Description
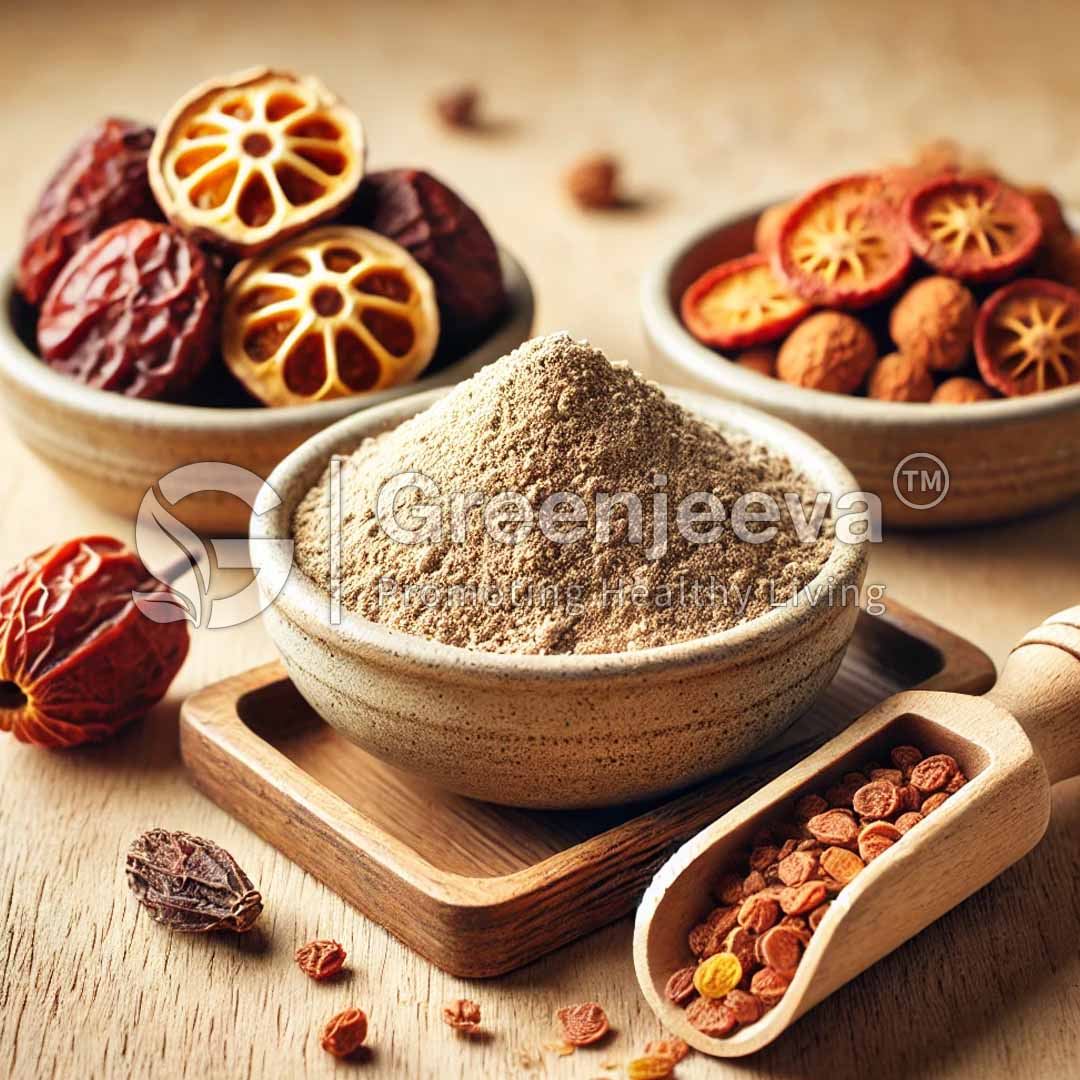
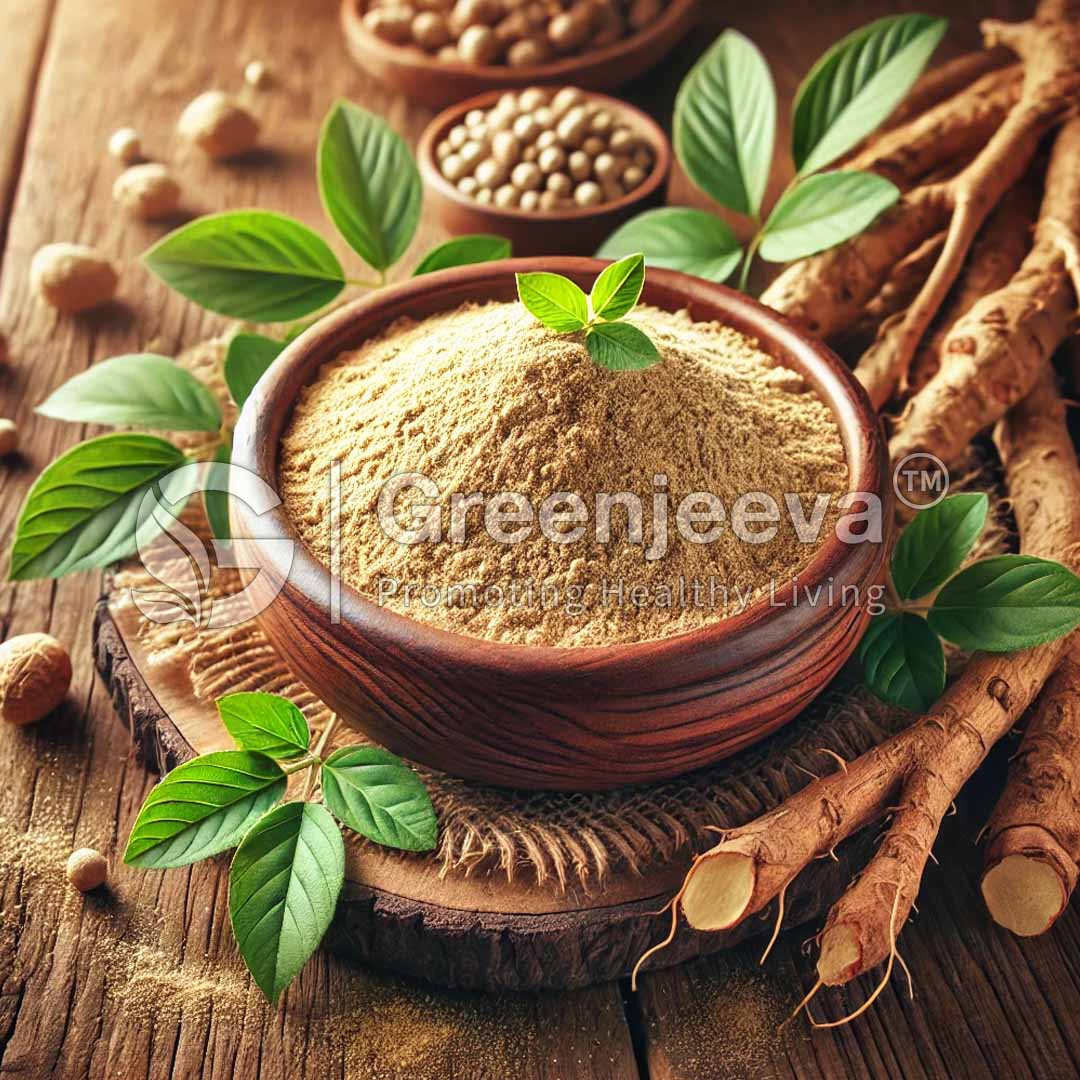
The term “Triphala” is taken from Sanskrit, meaning three fruits. Triphala is basically a mixture of dried fruits of three plants that are native to India. Those three plants are Amla or Emblica officinalis, Bibhitaki or Terminalia bellirica, and Haritaki or Terminalia Chebula. Since the ancient period, triphala has been used in Ayurvedic medicines. The major components in these fruits are tannins, gallic acid, ellagic acid, and chebulinic acid. It also contains quercetin, luteolin, saponins, anthraquinones, amino acids, and fatty acids. These bioactive components act as potent antioxidants.
Triphala is a traditional Ayurvedic herbal formulation that has been used for thousands of years in India and other parts of the world. The name Triphala comes from the Sanskrit words ‘tri’ meaning three and ‘phala’ meaning fruits, referring to the three fruits used in its production. The three fruits used in Triphala are Amalaki (Emblica officinalis), Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica), and Haritaki (Terminalia chebula). These fruits are grown in the rich soil of the Indian subcontinent and are harvested at their peak ripeness to ensure maximum potency.After harvesting, the fruits undergo thorough washing and cleaning to remove soil and impurities. Following the cleaning process, the fruits are dried using methods such as air-drying or low-temperature dehydration to preserve the integrity of their natural compounds. Once dried, the fruits are finely ground into a powder. This powder is then mixed in precise proportions, according to ancient Ayurvedic texts, to create the perfect balance of the three fruits. The blended Triphala powder is then packaged in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and maintain freshness, ensuring that it retains its quality and beneficial properties from production to application.