Description
Description
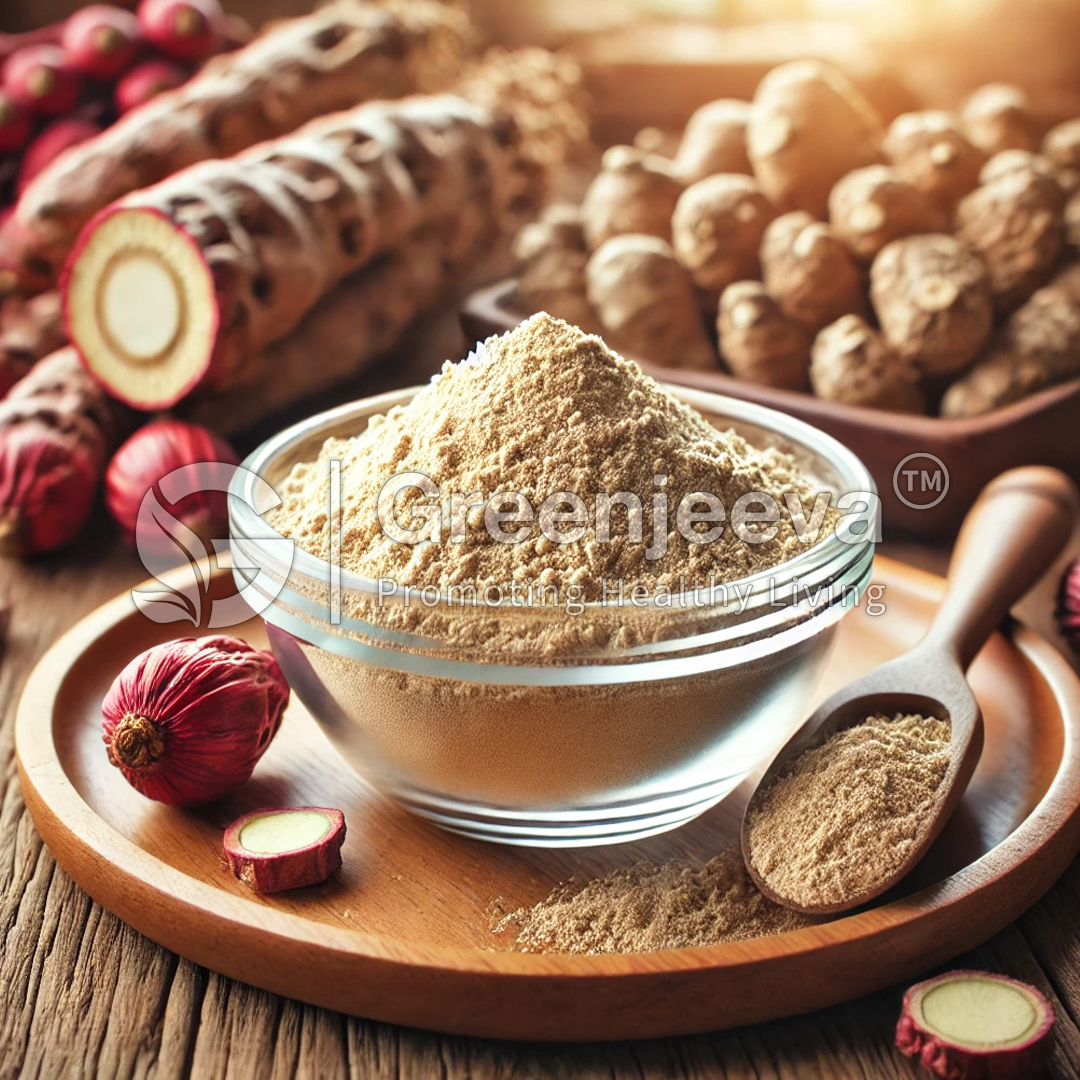
Maca is a root vegetable that belongs to the brassica family, which includes other cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale. It is typically grown in high altitudes of the Andes mountains, at elevations of over 12,000 feet. The harsh conditions in this region, including extreme temperatures, strong winds, and intense sunlight, make it a challenging environment for farming. However, these conditions are what contribute to maca’s unique properties and nutritional profile.
Traditionally, maca has been cultivated by small farmers in the central Peruvian Andes using traditional farming techniques. However, with the rise in demand for maca, commercial production has also increased. Today, maca is also grown in other regions of the world, including China, Bolivia, and the United States.
Maca is a hardy crop, and it can be grown in a variety of soils, including sandy, rocky, or clay soils. It is typically grown without the use of pesticides or fertilizers, making it an ideal option for organic farming. The plants typically take about eight months to reach maturity and are harvested by hand.
Once harvested, the roots of maca are washed, dried, and ground into a fine powder. This powder is then packaged and sold as a dietary supplement or used in various food products.